Введение
In the cold roll forming industry, profile design defines both the machine configuration and the final application. Unlike press-based forming, roll forming machines are optimized to produce long, constant cross-section profiles with high dimensional stability. These profiles are widely used in construction systems, industrial buildings, renewable energy structures, and light steel framing projects.

Understanding common roll forming profiles and their applications helps buyers select the correct roll forming machine configuration, tooling design, and auxiliary systems. This article summarizes the most widely used roll formed profiles in global markets and explains where and why they are applied.
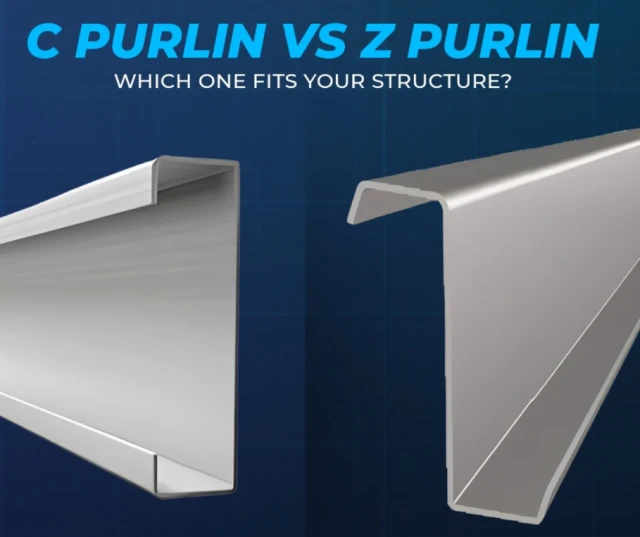
C, Z, and U Purlin Profiles
Profile Characteristics
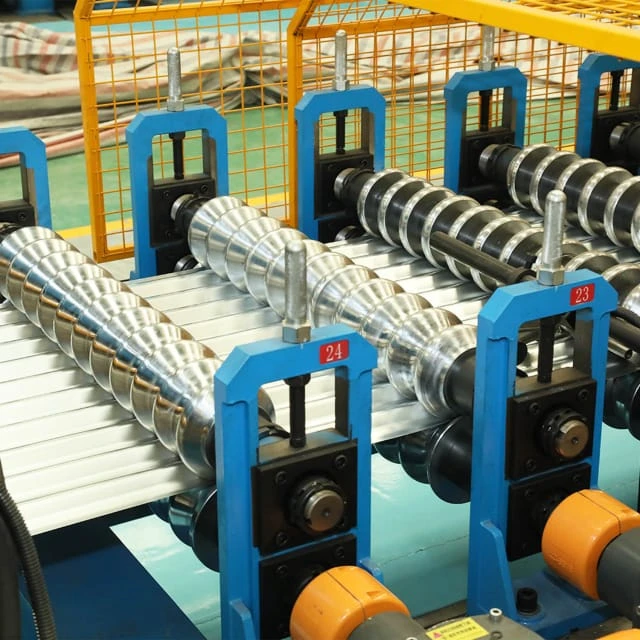
C, Z, and U sections are among the most common roll formed profiles in the steel construction industry. They are typically produced from galvanized or pre-painted steel coils using a purlin roll forming machine equipped with pre-punching, web-hole punching, and servo-controlled cutting systems.

- C Purlin: Symmetrical section, easy installation, widely used in industrial buildings
- Z Purlin: Offset flange design, suitable for overlapping installation in long-span roofs
- U Channel: Simple structure, often used for framing, supports, and edge members
- Sigma Purlin:Optimized cross-section design with enhanced load-bearing capacity and stiffness, ideal for long-span roofing and wall systems
These roll forming profiles are usually formed in thickness ranges from 1.5 mm to 3.0 mm, depending on structural load requirements.
Typical Applications
- Steel structure workshops and warehouses
- Agricultural buildings
- Portal frame structures
- Secondary roof and wall support systems
Roofing and Wall Panels
Roofing and Wall Panels are classic roll formed products known for their structural stiffness and cost efficiency. These profiles are produced at high speed on roofing sheet roll forming lines, often with hydraulic or servo-driven flying cut-off systems.
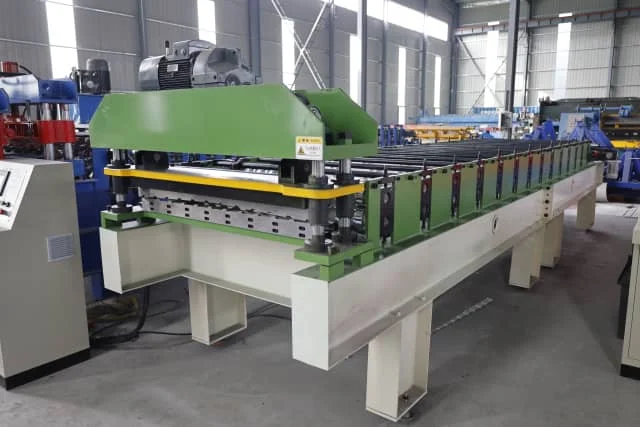

Common corrugation types include:
- Corrugated profiles
- Trapezoidal profiles
- Glazed profiles
Material thickness usually ranges from 0.25 mm to 0.6 mm, making production speed and surface quality critical.
Typical Applications
- Industrial roofing and wall cladding
- Temporary buildings and shelters
- Agricultural and storage facilities
- Emerging market construction projects
Metal Deck Profiles (Floor Deck & Roof Deck)
Profile Characteristics
Metal deck profiles are structural components formed using metal deck roll forming machines. These roll forming profiles feature deep ribs designed to improve load-bearing capacity and concrete bonding in composite floor systems.
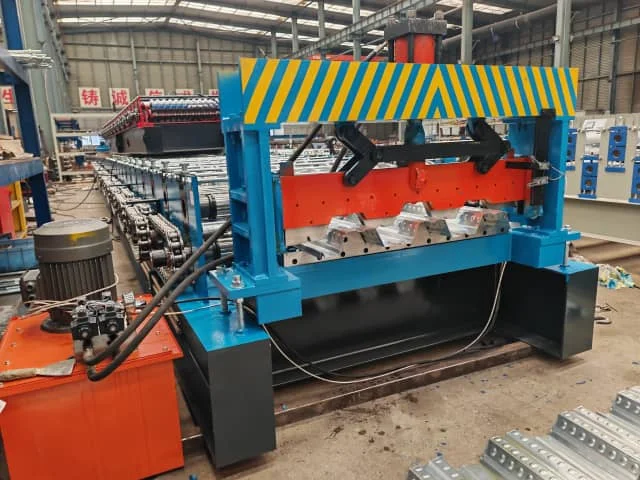

Deck profiles are typically classified as:
- Floor deck (composite deck)
- Roof deck (structural roof support)
- Form deck (temporary concrete formwork)
High-strength galvanized steel is commonly used, and tight tolerance control is essential.
Typical Applications
- Commercial buildings
- High-rise steel structures
- Industrial plants
- Parking structures
Light Gauge Steel Framing Profiles
Profile Characteristics
Light gauge steel framing (LGSF) profiles are produced using precision light gauge steel roll forming machines. Common sections include studs, tracks, joists, and bridging channels.
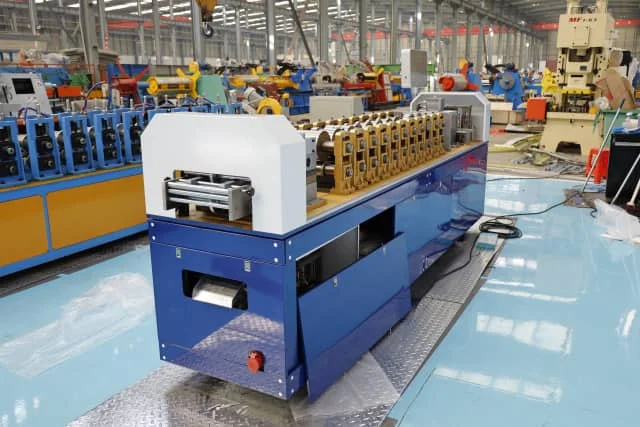

These roll forming profiles require:
- High dimensional accuracy
- Clean punching for service holes
- Minimal material distortion
Servo punching systems and inline labeling are often integrated into modern roll forming lines for LGSF production.
Typical Applications
- Prefabricated housing systems
- Modular buildings
- Interior wall partitions
- Commercial light steel structures
Solar PV Mounting Profiles
Profile Characteristics
Solar mounting profiles are specialized roll formed sections designed for photovoltaic support systems. These profiles are typically produced from galvanized or Zn-Al coated steel using solar PV mounting roll forming machines.
Common features include:
- Slotted holes for flexible installation
- High corrosion resistance
- Consistent length accuracy for on-site assembly
Typical Applications
- Ground-mounted solar power plants
- Rooftop PV systems
- Carport solar structures
- Utility-scale renewable energy projects
How Roll Forming Profiles Selection Impacts Roll Forming Machine Design
Each roll formed profile directly affects:
- Roller station quantity
- Roller material and heat treatment
- Drive system configuration
- Cutting method (flying cut-off vs stop-to-cut)
For this reason, experienced roll forming machine manufacturers focus on profile analysis and forming simulation before tooling production. Proper design reduces edge wave, bowing, and twist during high-speed production.
Заключение
Cold roll forming profiles are the foundation of modern steel construction and industrial manufacturing. From standard purlins and roofing sheets to advanced solar mounting rails and structural decks, roll formed sections offer unmatched efficiency, consistency, and scalability.
By understanding common roll forming profiles and their real-world applications, buyers can make informed decisions when selecting a Формовочный станок для металлопроката or complete линия прокатки. This knowledge also helps ensure long-term production stability and alignment with market demand.